Laboratory 7
Matrix Algebra
This laboratory activity aims to implement the principles and techniques of matrix operations. The student will be familiarized with the fundamental of matrix operations and learn how to apply them to solve equations.
The practices of the activity involve doing some operations between arrays and to be familiarized with it. This activity teaches and implies the techniques of some specific operations that are very vital to this course such as transposition and dot product. Meanwhile, the deliverables of this activity are to perform operations and prove the dot product properties. It was achieved by making a code with Python that will prove that the property is True.
Property 1 Flowchart
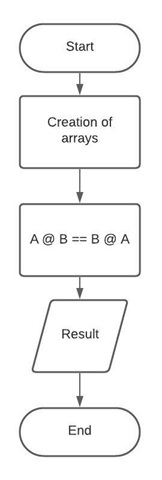
Figure above shows the flowchart created for proving the first property of the dot product. This property states that a dot product between A and B is not equal to the dot product between B and A.
Property 2 Flowchart
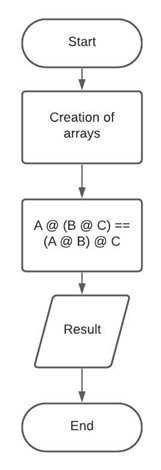
The second property of the dot product states that a dot product between matrix A and the result of the product between matrix B and C is equal to the dot product of matrix C between a dot product result between matrix A and B.
Property 4 Flowchart
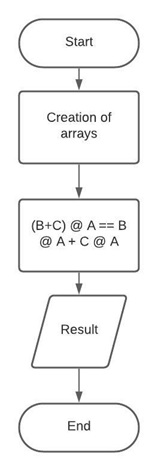
The fourth property of the dot product states that the dot product between A and the result from the addition between B and C is equal to the dot product between B and A added to the dot product between C and A.
Property 5 Flowchart
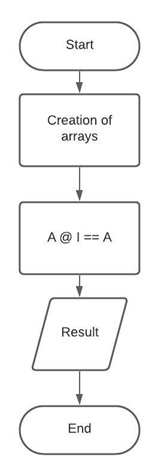
The fifth property of the dot product states that the dot product between a matrix and an identity matrix is equal to that matrix.
Property 6 Flowchart
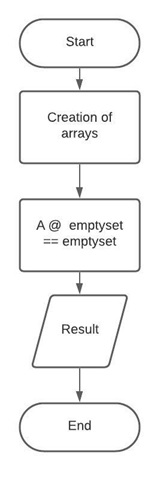
The sixth property of the dot product states that when a dot product between a matrix and a null set is performed, it will result in a null set or empty set.
Property 7 Flowchart
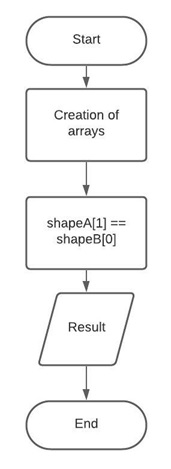
The seventh property of the dot product states that in A = (n,k) and B = (k,m), the column space size on A or (k) in A must equal to row space size on B or (k) in B to be able to perform dot product between matrices.
The results from implementing the properties of the dot product with Python for proving it are presented in this section
Property 1

Figure above shows that getting the equivalence of the two matrices that performed based on the first property results in False which proves that the property is right.
Property 2

Code snippet above shows that getting the equivalence of the two matrices that performed based on the second property results in True which proves that the property is right.
Property 4

Figure above shows the results from performing an equivalence test based on what the fourth property stated and it proves that this property is right.
Property 5

Code snippet above shows the proof that the dot product between an array and an identity array results in the array itself.
Property 6

Figure above shows the results from performing an equivalence test based on what the sixth property stated and it proves that this property is right.
Property 7

Code snippet above shows the proof of the dimension property. The shape of both matrices is shown first and since the column of the first matrix is equal to the number of rows in the second matrix, the dot product between the two matrices is successful.
So what’s this all about?
This laboratory successfully informed you about the implementation and the techniques of performing matrix operations such as transposition, dot product, inverse, and determinant. You was able to familiarize yourself with the different special properties of the dot product that become an activity for this laboratory. Moreover, you encountered how to do transposition, dot product, getting the determinant and the inverse of the matrix using Python and NumPy library.
Note:
The content above are the activities after the discussion so if you want to read and study the notebook that contains the discussion for this topic, kindly check the link for the repository at the end of this page.
Real-world application
According to [1], the problem of image reconstruction from projections can be considered as a system of linear equations of the form: Ax = B. It was explained thoroughly in [1] how it works but the main idea of this is that the system matrix A in simulates CT operation and the elements of this depend on the projection number and the angle. The values on the column of the matrix represent the intensities of the image and the column matrix b represents the collected projections by the scanner.
References
[1]L. Flores, V. Vidal, and G. Verdú, “System Matrix Analysis for Computed Tomography Imaging”, plos.org, 2015. [Online]. Available: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0143202. [Accessed: 12- Dec- 2020].